前言
最近项目中为了方便维护,底层统一使用C++编写。由于是项目是做屏幕共享sdk,所以只能底层的压缩、编解码使用C++,屏幕捕获部分Mac和win就自己实现了。那么问题就来了,因为是面向接口编程,所以项目的入口都是c++来写的,而屏幕捕获是需要oc部分的代码,就需要C++调用oc代码了。
准备
之前只做过OC调动C++,于是Google了一下,在Stack Overflow上找到了这个回答。要看具体描述的可以去链接看看,实现思路一共有两种,我在这里大概描述一下。第一种,由于C++是不能直接调用OC的,所以需要通过C语言作为中间层,即C++调用C,C调用OC,这样就达到了C++调用OC的目的。第二种OC是可以调用C++的,通过在外部声名C++类,然后类具体实现放在OC类中,这样C++类就能够调用OC类了,其他需要调用OC的类,只需要调用外部声名的类即可。
实现
具体的实现方式有两种,第一种是C语言方法接收oc对象指针和参数,然后把指针桥接为具体的oc对象。第二种是用C++进行包装,先声名一个C++类,这里称为A。然后在OC类中,这里称为B,对A进行实现,因为这个实现实在OC语言里的,所以在这里是可以直接调用OC代码的。接下来声名一个C++类C。类C通过持有类A来调用OC类B,即A(C++)->C(C++)->B(OC类)
## 实现方式一 by C
MyObject-C-Interface.h
1
int MyObjectDoSomethingWith (void *myObjectInstance, void *parameter);
MyObject.h
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8 @interface MyObject : NSObject
{
int someVar;
}
- (int)doSomethingWith:(void *)aParameter;
@end
MyObject.mm
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22 @implementation MyObject
int MyObjectDoSomethingWith (void *self, void *aParameter)
{
// 通过将self指针桥接为oc 对象来调用oc方法
return [(__bridge id)self doSomethingWith:aParameter];
}
- (int) doSomethingWith:(void *) aParameter
{
//将void *指针强转为对应的类型
int* param = (int *)aParameter;
return *param / 2 ;
}
- (void)dealloc
{
NSLog(@"%s", __func__);
}
@end
MyCPPClass.h
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11 class MyCPPClass {
public:
MyCPPClass();
~MyCPPClass();
int someMethod (void *objectiveCObject, void *aParameter);
void *self;
void setSelf(void *self);
};
MyCPPClass.cpp
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
#include "MyObject-C-Interface.h"
MyCPPClass::MyCPPClass()
{
}
MyCPPClass::~MyCPPClass()
{
}
int MyCPPClass::someMethod (void *objectiveCObject, void *aParameter)
{
// To invoke an Objective-C method from C++, use
// the C trampoline function
return MyObjectDoSomethingWith (objectiveCObject, aParameter);
}
void MyCPPClass::setSelf(void *aSelf)
{
self = aSelf;
}
main.mm
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
#include "MyCPPClass.hpp"
#import "MyObject.h"
int main(int argc, const char * argv[]) {
@autoreleasepool {
// insert code here...
NSLog(@"Hello, World!");
MyObject *object = [[MyObject alloc] init];
MyCPPClass *c = new MyCPPClass();
c->setSelf((__bridge void *)object);
int a = 12;
int result = c->someMethod((__bridge void *)object, &a);
NSLog(@"%d", result);
}
return 0;
}
运行结果如下:
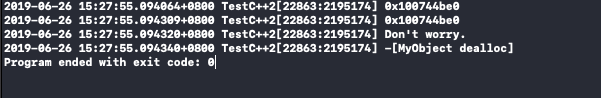
存在的问题
在每次C++调用时都需要传递OC对象桥接为==void ==的指针,使用起来很不方便。
## 方式二 by C++ IMPL
*MyObject-C-Interface.h**
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18 #ifndef MyObject_C_Interface_h__h
#define MyObject_C_Interface_h__h
class MyClassImpl
{
public:
MyClassImpl ( void );
~MyClassImpl( void );
void init( void );
int doSomethingWith( void * aParameter );
void logMyMessage( char * aCStr );
private:
void * self;
};
#endif /* MyObject_C_Interface_h__h */
需要注意的是,==MyClassImpl==的实现是放在OC中的
MyObject.h
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14 NS_ASSUME_NONNULL_BEGIN
@interface MyObject : NSObject
{
int someVar;
}
- (int) doSomethingWith:(void *) aParameter;
- (void) logMyMessage:(char *) aCStr;
@end
NS_ASSUME_NONNULL_END
MyObject.mm
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67 #include "MyObject-C-Interface.h"
typedef void(^RetainSelfBlock)(void);
@implementation MyObject
{
RetainSelfBlock _retainBlock;//通过这个block持有对象,造成循环引用,避免被释放
}
MyClassImpl::MyClassImpl( void )
: self( NULL )
{
}
MyClassImpl::~MyClassImpl( void )
{
[(__bridge id) self breakRetainCycly];
}
void MyClassImpl::init( void )
{
MyObject *object = [[MyObject alloc] init];
object->_retainBlock = ^{//循环引用
[object class];
};
self = (__bridge void *)object;
NSLog(@"%p", self);
}
int MyClassImpl::doSomethingWith( void *aParameter )
{
NSLog(@"%p", self);
return [(__bridge id)self doSomethingWith:aParameter];
}
void MyClassImpl::logMyMessage( char *aCStr )
{
[(__bridge id)self logMyMessage:aCStr];
}
- (int) doSomethingWith:(void *) aParameter
{
int result = 0;
// ... some code to calculate the result
return result;
}
- (void) logMyMessage:(char *) aCStr
{
NSLog( @"%s", aCStr );
}
//打破循环引用,释放对象
- (void) breakRetainCycly
{
_retainBlock = nil;
}
- (void)dealloc
{
NSLog(@"%s", __func__);
}
@end
在==MyObject.mm==中需要注意的是,由于OC是使用ARC来进行内存管理的,C++不能够管理OC对象的生命周期。在默认的情况下,临时变量会在autorelease pool每一次pop后被释放,所以在oc实现中要想对象不被释放,那就需要循环引用来帮忙了。
具体代码如下,在MyClassImpl初始化时,利用循环引用保证object不被释放,在MyClassImpl调用析构函数时,将block置空,打破循环引用,以此来释放oc对象
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22 void MyClassImpl::init( void )
{
MyObject *object = [[MyObject alloc] init];
object->_retainBlock = ^{//循环引用
[object class];
};
self = (__bridge void *)object;
NSLog(@"%p", self);
}
MyClassImpl::~MyClassImpl( void )
{
[(__bridge id) self breakRetainCycly];
}
//打破循环引用,释放对象
- (void) breakRetainCycly
{
_retainBlock = nil;
}
MyCPPClass.hpp
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24 #ifndef MyCPPClass_hpp
#define MyCPPClass_hpp
#include <stdio.h>
class MyClassImpl;
class MyCPPClass
{
enum { cANSWER_TO_LIFE_THE_UNIVERSE_AND_EVERYTHING = 42 };
public:
MyCPPClass ( void );
~MyCPPClass( void );
void init( void );
void doSomethingWithMyClass( void );
private:
MyClassImpl * _impl;
int _myValue;
};
#endif /* MyCPPClass_hpp */
MyCPPClass.cpp
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30 #include "MyCPPClass.hpp"
#include "MyObject-C-Interface.h"
MyCPPClass::MyCPPClass( void )
: _impl ( NULL )
{ }
void MyCPPClass::init( void )
{
_impl = new MyClassImpl();
_impl->init();
}
MyCPPClass::~MyCPPClass( void )
{
if ( _impl ) { delete _impl; _impl = NULL; }
}
void MyCPPClass::doSomethingWithMyClass( void )
{
int result = _impl->doSomethingWith(&_myValue);
if ( result == cANSWER_TO_LIFE_THE_UNIVERSE_AND_EVERYTHING )
{
_impl->logMyMessage("Hello, Arthur!");
}
else
{
_impl->logMyMessage("Don't worry.");
}
}
main.mm
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11 #include "MyCPPClass.hpp"
int main(int argc, const char * argv[]) {
@autoreleasepool {
MyCPPClass *temp = new MyCPPClass();
temp->init();
temp->doSomethingWithMyClass();
delete temp;
}
return 0;
}
运行结果
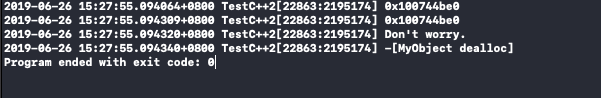
# 总结
第一种通过C语言的方式来调用,使用起来更复杂,所以建议使用C++的方式来实现。需要注意的问题是C++不能管理OC对象的释放,所以需要利用循环引用。
你可以在这里下载demo
参考:https://stackoverflow.com/questions/1061005/calling-objective-c-method-from-c-member-function